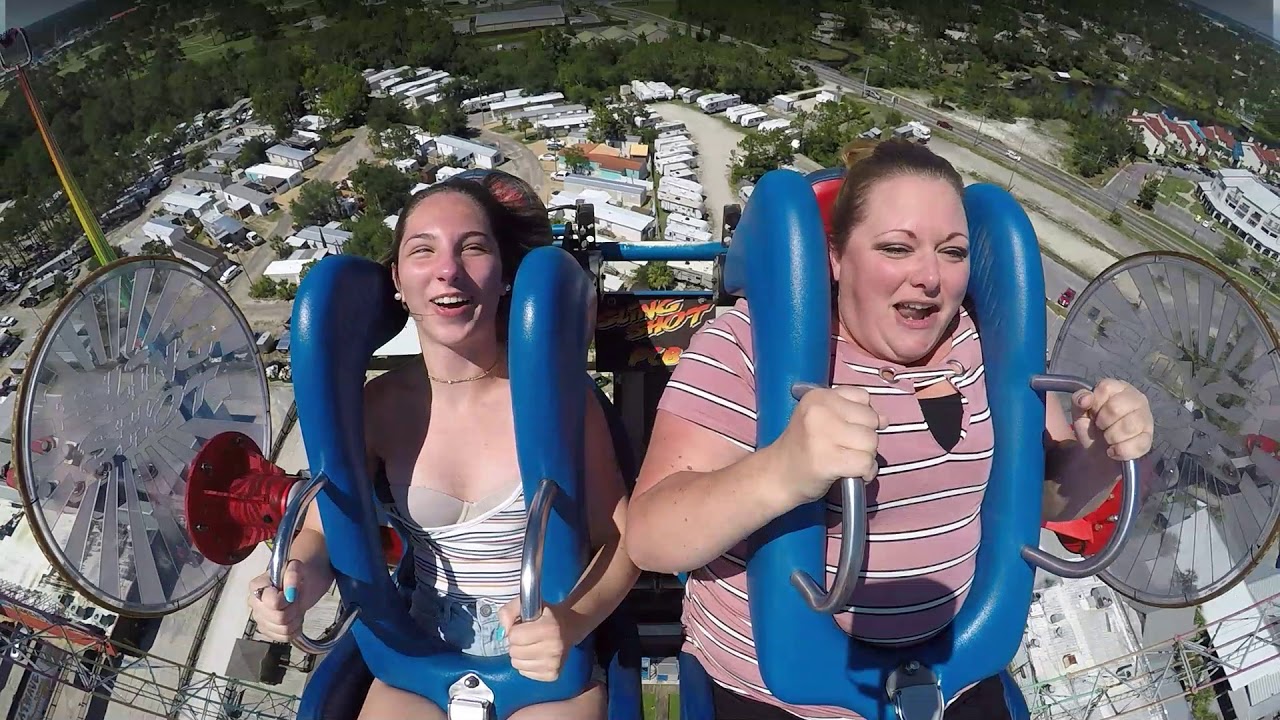What are the safety considerations for amusement park rides involving a sudden launch? A crucial component of ride safety is a properly functioning restraint system.
A malfunctioning or improperly fitted restraint system on a launch-based amusement ride can have catastrophic consequences. This system, often involving harnesses and straps, is designed to securely hold riders during the high-acceleration phases of the ride. A "slip" in this context refers to a failure of the restraint to maintain a secure hold on the rider. Such a failure might be due to a defect in the hardware, improper installation, or user error. A real-world example of this issue might be a harness strap that loosens during the launch phase or a quick-release mechanism that unexpectedly activates.
The importance of this system cannot be overstated. The sudden acceleration and deceleration forces involved in these kinds of rides can cause significant stress on the human body. Proper restraints are vital to preventing injuries ranging from minor abrasions and sprains to more serious head trauma or ejection from the ride. The safety of the riders is paramount in designing and operating amusement park attractions, and the reliability of restraint systems is critical. The historical context of this involves the evolution of ride technology and safety regulations, reflecting the increasing focus on preventing accidents.
Moving forward, we will examine specific safety protocols and regulations pertaining to launch-based amusement rides, including industry best practices, rider responsibilities, and the role of park maintenance.
Slingshot Ride Slip
Safety is paramount in launch-based amusement rides. A critical component is the integrity of the restraint system, preventing rider ejection or injury. A "slip" refers to a failure of this system, potentially leading to severe consequences.
- Restraint Failure
- Rider Ejection
- Safety Regulations
- Inspection Procedures
- Maintenance Protocols
- Emergency Response
Restraint failure is the core issue. Rider ejection is a direct consequence, with safety regulations ensuring minimal risk. Thorough inspection and maintenance protocols mitigate this risk. Emergency response plans address potential accidents, illustrating the interconnected nature of these aspects. For example, a malfunctioning harness, failing to secure a rider during launch, exemplifies restraint failure, leading to rider ejection, and prompting immediate safety protocols, ensuring the safety and well-being of all involved.
1. Restraint Failure
Restraint failure, a critical safety concern in launch-based amusement rides, is intricately linked to the concept of a "slingshot ride slip." Understanding the potential causes and consequences of restraint failure is essential for ensuring the safety of riders. This exploration delves into key facets of such failures, highlighting their implications for ride safety.
- Design Flaws and Manufacturing Defects
Inadequate design or manufacturing flaws in the restraint system itself can lead to premature wear, component failure, or an inability to withstand the forces of launch. Examples include improperly sized or installed buckles, defective harness webbing, or structural weaknesses in the supporting frame. These defects directly compromise the integrity of the restraint, increasing the risk of slippage during the ride and potentially resulting in rider injury or ejection.
- Maintenance Neglect and Deterioration
Consistent maintenance and inspection are crucial to ensuring the ongoing reliability of the restraint system. Neglect in these areas can lead to the gradual deterioration of components, increasing the likelihood of a failure during the ride. Examples include missed or inadequate inspections, the accumulation of wear and tear, the neglect of scheduled maintenance, and ignoring early warnings of potential issues. This neglect creates a dangerous environment where the restraint system may fail during a launch cycle, potentially leading to a slip.
- Operator Error and Misuse
Human error can also be a contributing factor to restraint failure. Incorrect installation or adjustment of the restraint by operators, inadequate supervision, or failures to adhere to established procedures compromise the system's effectiveness. Improper training of personnel handling the ride equipment is another contributor. For instance, an incorrectly fastened harness or an operator failing to double-check a restraint before launch can lead to a slip and subsequent rider injury.
- Environmental Factors and External Forces
Environmental factors, such as extreme temperatures or exposure to corrosive substances, can also degrade materials and components over time. External forces like impacts or sudden jolts unrelated to the launch mechanism can also compromise the structural integrity of the restraint. For instance, a sudden impact might dislodge or weaken a vital component of the harness system, leading to a slip.
In conclusion, understanding the various facets of restraint failure is crucial to mitigating the risks associated with "slingshot ride slip." Proactive measures, including rigorous design, robust maintenance schedules, meticulous operator training, and careful consideration of environmental factors, contribute to the safety of riders on launch-based amusement rides. A comprehensive approach to prevent restraint failure is essential for preserving rider safety.
2. Rider Ejection
Rider ejection, a grave concern in the context of launch-based amusement rides, is a direct consequence of malfunctions in the restraint system. A "slingshot ride slip," often stemming from restraint failure, is a critical factor in such incidents. Understanding the mechanics of rider ejection, linked inextricably to restraint failures, is crucial for developing robust safety protocols.
- Impact Forces and Injury Mechanisms
The high acceleration forces inherent in launch-based rides, when coupled with a restraint failure, generate substantial impact forces on riders. These forces can lead to severe injuries, from minor abrasions and contusions to significant fractures, head trauma, or internal organ damage. Understanding the physics of impact is critical to designing restraint systems capable of withstanding these forces. Examples include instances where riders are ejected from their harnesses at launch, resulting in impact with the ride structure or the ground.
- Restraint System Failures and Ejection Scenarios
Specific types of restraint failures can directly cause ejection. Examples include faulty harnesses, straps that snap or loosen under pressure, inadequate securing mechanisms, malfunctions in quick-release systems, or failures in the supporting structure of the restraint. Analyzing the various failure points within the restraint system is key to identifying potential areas of weakness. The scenarios often involve a cascading effect, where a seemingly minor defect can lead to catastrophic consequences during launch.
- Environmental Considerations and Potential Impacts
Environmental factors can influence rider ejection. Extreme weather conditions, debris, or unexpected external impacts can compromise the restraint system's effectiveness, leading to ejection. Maintaining the restraint system's structural integrity in various environmental situations is essential for safety. Examples might include strong winds affecting the stability of a harness or a piece of debris striking a critical part of the restraint assembly, thereby triggering a slip and ejection.
- Regulatory Compliance and Mitigation Strategies
Rigorous safety regulations, encompassing design specifications, maintenance protocols, and emergency response procedures, aim to minimize the risk of rider ejection. Adequate training of ride operators, thorough inspections of the restraint systems before each use, and emergency procedures tailored to specific ride types are vital aspects of mitigation. Understanding compliance with these standards helps prevent future incidents by highlighting and addressing systemic risks.
In conclusion, rider ejection, a potential outcome of a "slingshot ride slip," highlights the critical need for comprehensive safety measures in the design, operation, and maintenance of launch-based amusement rides. Proactive measures, encompassing meticulous inspections, rigorous training protocols, and adherence to safety regulations, are paramount in minimizing the risk of such events and ensuring the safety of riders.
3. Safety Regulations
Safety regulations are fundamental to mitigating the risks associated with launch-based amusement rides, including the potential for "slingshot ride slip." These regulations, encompassing design standards, operational protocols, and maintenance procedures, are instrumental in ensuring rider safety and preventing incidents. A comprehensive understanding of these regulations is critical for identifying potential weaknesses and implementing preventative measures to reduce the risk of accidents.
- Design Standards
Regulations dictate the minimum design specifications for restraint systems, including materials, strength requirements, and redundancy provisions. These specifications aim to ensure the system can withstand the extreme forces generated during launch and maintain a secure hold on riders. Compliance with these standards is crucial in preventing failures that can lead to rider ejection or injury during a slingshot ride. Examples include testing protocols for harness strength under various loads and the incorporation of backup mechanisms.
- Maintenance Protocols
Regular inspection and maintenance protocols for restraint systems are crucial. Regulations outline specific inspection schedules, procedures, and documented record-keeping requirements. This ensures that the system remains in optimal working condition, preventing gradual deterioration that can compromise its integrity and increase the risk of a slip. This includes thorough checks for wear, damage, and malfunctioning components.
- Operational Protocols and Training
Regulations dictate procedures for pre-ride checks, operator training, and emergency response protocols. This encompasses verifying the secure attachment of restraints, conducting pre-ride safety checks for the restraint systems, and having trained personnel available for handling potential incidents. Compliance with these protocols helps minimize the potential for human error and enhances the overall safety culture around the ride.
- Emergency Procedures and Response Mechanisms
Regulations mandate specific emergency procedures, including evacuation protocols and communication plans, to address and handle potential incidents. This includes immediate response protocols for incidents involving restraint failures or rider ejection. These regulations ensure timely action to mitigate the consequences of a slip and facilitate swift and effective recovery.
In summary, safety regulations provide a framework to address the risk of "slingshot ride slip." By establishing rigorous design standards, maintenance protocols, operational procedures, and emergency responses, these regulations create a safer environment for riders on launch-based rides. Compliance with and adherence to these regulations are crucial for minimizing the potential for accidents and ensuring rider well-being.
4. Inspection Procedures
Rigorous inspection procedures are paramount in preventing incidents like "slingshot ride slip." These procedures form the bedrock of safety protocols, ensuring the integrity of restraint systems and minimizing the risk of rider injury or ejection. Failure to adhere to established inspection protocols can compromise the structural integrity of the system, thereby directly increasing the likelihood of a critical failure during operation.
- Pre-Operational Checks
Thorough pre-operational checks encompass a systematic examination of all components of the restraint system, including harnesses, straps, buckles, and connecting mechanisms. Visual inspections for wear, damage, or any signs of compromised integrity are essential. Examples include verifying the proper tension and secure attachment of all straps, checking for frayed webbing, examining buckles for proper locking mechanisms, and inspecting support structures for any signs of stress or damage. Failure to identify and address these issues before operation creates a high-risk environment, increasing the possibility of a slip during a launch cycle.
- Regular Maintenance Schedules
Established schedules for routine maintenance ensure consistent checks for deterioration and address any emerging safety concerns before they escalate. These schedules involve a structured process of inspection, identifying and correcting potential problems, and documenting all findings. Examples include scheduled inspections conducted after a specific number of usage cycles, weather-related inspections, or inspections following any significant events. Consistent maintenance mitigates the risk of gradual deterioration and consequent failure of the restraint system during operation, ultimately reducing the chance of a "slingshot ride slip."
- Detailed Documentation and Reporting
Comprehensive documentation of inspection findings is crucial for tracking maintenance history. Detailed records provide a historical context to identify patterns, pinpoint potential areas for improvement, and demonstrate compliance with safety standards. Examples include meticulously documented inspection reports, photographs of any discovered damage, and a detailed record of maintenance actions taken. Effective documentation aids in identifying potential trends and facilitates proactive measures to mitigate risks, thereby reducing the potential for a "slingshot ride slip" through preventative maintenance.
- Calibration and Testing
Routine calibration and testing of critical components ensure that safety mechanisms operate as intended. This often includes stress tests to assess the structural integrity of the restraint system under expected operational forces. Examples include testing the resistance of buckles and straps to specified tensile loads, evaluating the integrity of the entire restraint system under simulated launch conditions, and checking for adherence to manufacturer specifications. Regular calibration and testing are vital in maintaining the reliability of the system and prevent catastrophic failures, limiting the risk of a "slingshot ride slip."
In conclusion, thorough inspection procedures, encompassing pre-operational checks, scheduled maintenance, detailed documentation, and calibration/testing, are essential to minimizing the risk of "slingshot ride slip." These procedures are not merely compliance measures but are integral to maintaining the safety and reliability of the ride, creating an environment where a "slingshot ride slip" becomes significantly less likely.
5. Maintenance Protocols
Maintenance protocols are fundamental to preventing incidents like "slingshot ride slip." Effective protocols directly influence the reliability and safety of launch-based amusement rides. Inadequate maintenance can lead to critical component failures, creating a direct link between neglected upkeep and the potential for a catastrophic malfunction during a launch sequence. Neglecting scheduled inspections, failing to address minor wear and tear, and ignoring early warning signs all contribute to a progressively hazardous environment, increasing the risk of a "slingshot ride slip." A compromised restraint system, weakened by inadequate maintenance, is significantly more vulnerable to failure during the intense forces of a launch. This failure can manifest as loosened straps, broken buckles, or fractured components, directly leading to rider ejection or injury. For example, a missed inspection that fails to detect a frayed harness strap could result in a catastrophic failure during the launch, causing a "slingshot ride slip" and serious injury.
The practical significance of understanding this connection is clear. Regular maintenance, encompassing visual inspections, functional checks, and component replacements, is crucial in maintaining ride safety. This proactive approach minimizes the probability of a "slingshot ride slip" by identifying and addressing potential issues before they become critical. Implementing and consistently adhering to rigorous maintenance protocols is essential for amusement park operators. This involves not only adhering to manufacturer recommendations for maintenance schedules but also consistently evaluating and adjusting protocols based on real-world operating conditions. Understanding the specific stresses and forces a ride experiences over time is essential for adapting maintenance strategies and mitigating risks. Effective maintenance logs, including detailed records of inspections, repairs, and replacements, provide crucial data for identifying potential trends and improving protocols. This historical data, along with analysis of previous incidents, can inform preventative measures to reduce the risk of future "slingshot ride slips." Furthermore, well-documented protocols offer demonstrable evidence of adherence to safety standards, a critical aspect for regulatory compliance.
In conclusion, maintenance protocols are inextricably linked to the prevention of "slingshot ride slip." Neglecting these protocols compromises the safety of the ride and those using it. Proactive and comprehensive maintenance strategies, including regular inspections, timely repairs, and adherence to safety guidelines, are essential in creating and sustaining a safe environment. By acknowledging the direct correlation between inadequate maintenance and the risk of a "slingshot ride slip," amusement park operators can proactively implement strategies to minimize potential hazards and ensure the well-being of their patrons.
6. Emergency Response
Effective emergency response is inextricably linked to the potential for "slingshot ride slip" incidents. A well-defined and practiced emergency response plan is crucial for mitigating the consequences of a malfunction, preventing escalation of an incident, and ensuring the safety of riders and personnel. The plan must address the specific hazards associated with the ride, including the rapid acceleration and deceleration forces that, when coupled with a restraint system failure, can lead to potentially severe rider injuries or even ejection. A "slingshot ride slip" can trigger a cascade of events necessitating a swift and coordinated response.
The importance of emergency response in the context of a "slingshot ride slip" is multifaceted. A prompt and well-executed response minimizes injuries, preventing secondary hazards like panic and uncontrolled movement. Pre-planned communication protocols and designated roles for personnel, coupled with readily accessible emergency equipment and personnel, are vital elements. Emergency response systems must factor in evacuation procedures, first aid provision, and communication channels to external support services, such as medical professionals and emergency responders. Training exercises, simulating various potential incidents, are critical to ensure staff can react effectively under pressure and in a coordinated manner. For example, a prompt response to a restraint failure during a launch sequence could prevent a rider from sustaining severe injuries from impact with ride components or the ground. Real-world incidents demonstrate how a delayed or inadequate response has potentially amplified damage or contributed to further harm.
In conclusion, the effectiveness of emergency response in managing "slingshot ride slip" scenarios directly correlates with the safety and well-being of all involved. Comprehensive planning, rigorous training, and prompt implementation of procedures are essential for mitigating the risks and consequences associated with such incidents. Failure to have robust emergency protocols in place significantly increases the potential for harm and underscores the critical importance of this component in the overall safety infrastructure of launch-based amusement rides.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common concerns and misconceptions surrounding "slingshot ride slip" incidents, focusing on safety protocols and preventative measures. The information presented is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional guidance.
Question 1: What constitutes a "slingshot ride slip"?
A "slingshot ride slip" describes a failure of the restraint system on a launch-based amusement ride. This failure can manifest as a loosening, breakage, or malfunction of the harness, straps, or other securing mechanisms. This ultimately compromises the ability of the system to maintain a secure hold on the rider during the ride's launch phase. The result can lead to rider ejection.
Question 2: What are the potential causes of a "slingshot ride slip"?
Potential causes include design flaws or manufacturing defects in the restraint system, inadequate or neglected maintenance, operator error, misuse of the ride, or environmental factors impacting component integrity. These can range from faulty buckles to weakened straps, or even external forces acting on the system during operation. Understanding the range of potential causes is crucial for implementing preventative strategies.
Question 3: What are the safety implications of a "slingshot ride slip"?
The consequences can be severe, ranging from minor injuries like abrasions and contusions to significant trauma like fractures, head injuries, and internal organ damage, depending on the nature and severity of the slip. The impact forces exerted on the rider during an ejection incident can have lasting effects. The potential for serious harm underscores the importance of proactive safety measures and compliance with regulations.
Question 4: How can a "slingshot ride slip" be prevented?
Prevention relies on a combination of factors. Rigorous design standards, comprehensive maintenance protocols, meticulous operator training, and strict adherence to safety regulations are crucial. These elements include regular inspections, maintenance schedules, calibration checks, and the implementation of emergency response plans. A proactive approach, encompassing all aspects of ride operation, is essential for reducing the likelihood of a "slingshot ride slip."
Question 5: What should riders do to ensure safety on launch-based amusement rides?
Riders should carefully follow all instructions and guidelines provided by ride operators and park personnel. Attending to safety briefings and carefully adhering to the rules is paramount. Riders should promptly address any concerns about the ride's condition or potential hazards. Active participation in safety protocols, demonstrating a responsible attitude, is crucial to minimizing individual risks.
Understanding the preventative measures and potential consequences associated with "slingshot ride slip" incidents is essential for maintaining a safe environment on launch-based amusement rides. A combination of proactive maintenance, adherence to safety regulations, and vigilant response procedures are necessary to minimize risks and ensure the safety of all involved.
The next section will examine specific safety protocols and regulations.
Conclusion
This exploration of "slingshot ride slip" highlights the critical interrelationship between ride design, maintenance, and emergency response protocols. The potential for catastrophic consequences, ranging from minor injuries to severe trauma, underscores the paramount importance of a comprehensive safety framework. Key elements, including meticulous inspection procedures, rigorous maintenance schedules, adherence to safety regulations, and well-defined emergency response plans, were found to be inextricably linked to minimizing the risk of such incidents. The analysis emphasizes the multifaceted nature of safety, demonstrating how failures in any single component of the safety infrastructure can contribute to a system-wide risk. Understanding the potential causes of restraint system malfunctions, ranging from design flaws and material degradation to operator error and environmental factors, is crucial for developing preventative measures.
The conclusion unequivocally demonstrates the need for continuous improvement and vigilance in the operation and maintenance of launch-based amusement rides. Proactive measures, coupled with rigorous adherence to safety standards, are essential to ensure the safety and well-being of all patrons. Future research should investigate the development of predictive maintenance strategies, advanced safety technologies, and innovative approaches to emergency response protocols. The industry must prioritize consistent evaluation and refinement of safety practices to create a truly secure environment. Neglecting these considerations carries substantial risks. This ongoing commitment to safety, evident in every facet of ride operation and management, ultimately safeguards the public and upholds the integrity of the industry.
You Might Also Like
Lara Rose Nude Photos: Hottest Pics & VideosIzzy On Grey's Anatomy: A Deep Dive
Geno & Nico: Where Are They Now? [Update 2023]
Best Bollywood Movies & Shows On BollyFilx
Is Brittany Force Married? The Truth!
Article Recommendations
- Donald Trump Police Immunity
- Exploring Musialas Religion Faith And Personal Beliefs Of A Football Prodigy
- Unveiling The Stature Of Alex Pereira Understanding His Height And Impact
![Slingshot ride boob slip [053] r/ytnsfw](https://i2.wp.com/external-preview.redd.it/slingshot-ride-boob-slip-0-53-v0-Q2KnvDqLzs8YMUvk_iTvPEhLEASsUUr5Ukngv3dFhEs.jpg?auto=webp&s=861a3b09e911509bb3c87d2d910bdca325186cf0)